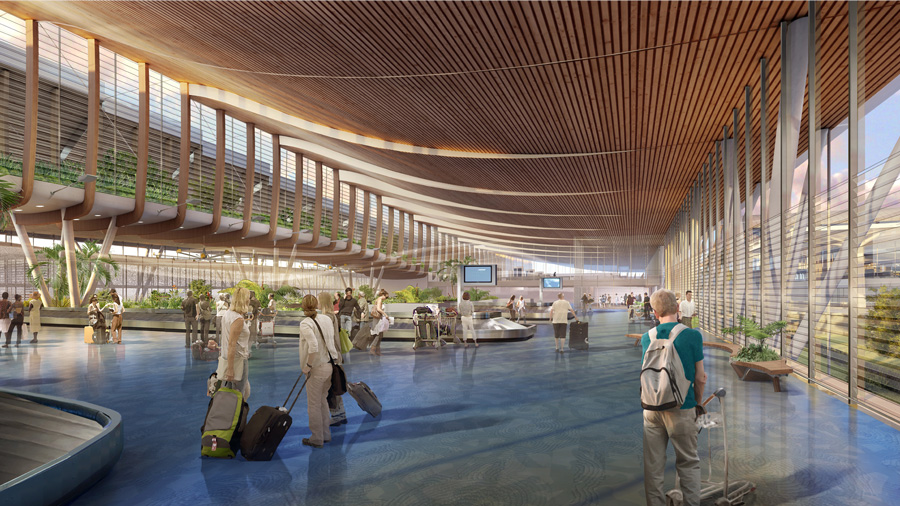
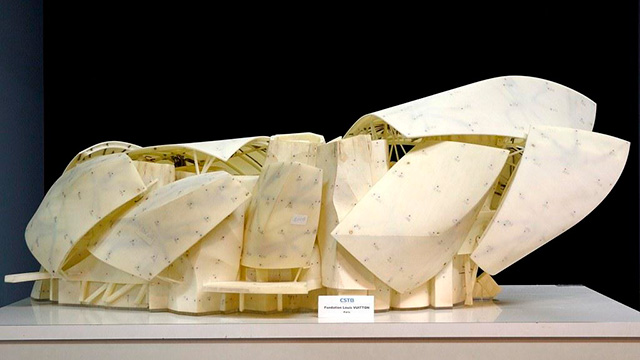
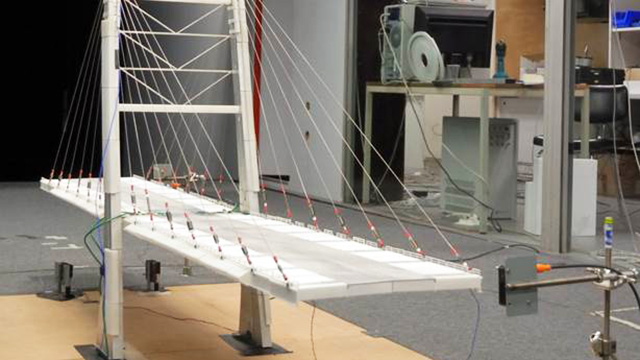
The CSTB is the preferred partner of major construction projects in France and around the world. High-rises, stadiums, museums and bridges: all these architectural and civil engineering structures are regularly tested and assessed by our experts. The CSTB can work in the initial phases of a project, right from the first sketches and impact studies, during the different phases of construction and even beyond the completed project, to monitor its evolution over time.
Climatology
On-site measurements
Our services
- Characterization of the weather conditions at the location chosen for the structure: wind, sun radiation, temperature and precipitation.
References
Statistical studies
Our services
- Statistical analysis and mapping of the site's extreme weather events: extreme wind speeds, simultaneous rain and wind, snow and hail load, maximum temperature, etc.
References
Digital simulations
Our services
- Analysis of the risks in connection with extreme weather conditions: temperature (heat waves and extreme cold), wind (storms and tornadoes) and precipitation (flooding).
References
Wind loading and comfort
Using an experimental approach Small-scale study, Full-scale study
- Analysis of the effects of the wind on the basis of expertise and a regulatory approach (Eurocodes): calculation of the benchmark speed, theoretical and experimental characterization of site effects on cranes, in conformity with R406.
- Preliminary wind loading studies of buildings.
-
Analysis of the aerodynamic forces exerted on buildings:
- local loads exerted on envelopes;
- total loads, calculation of the dynamic contribution.
- Dynamic response of flexible structures in small-scale aeroelastic models, aerodynamic stability of bridge decks, prediction of the structure's response to turbulent wind.
- Study of the behavior of completed works, characterization of the modal response to excitation caused by the wind or pedestrian traffic (footbridges).
- Study of the wind resistance and vibration behavior of small structures.
- Study of the aeroacoustic behavior of structures.
- Study of the behaviors of structures subjected to high Reynolds number flows, marine or oil applications and the offshore industry.
- Simulation of mesoscale and small-scale atmospheric flows in urban environments and on complex reliefs; on-site calculation of wind characteristics.
- Modeling of driving rain phenomena, estimation of the risk of people getting wet in semi-open spaces.
- Calculation of the transport of pollutants and plume behavior, accounting for thermal phenomena.
- Defining the aerothermal properties of large volumes.
- Simulation of indoor ventilation systems.
Technological platforms
- Jules Verne climatic wind tunnel for small-scale or full-scale prototypes.
- Atmospheric wind tunnels for reduced scale models.
- Metrology: pressures 1000 channels at 1000 Hz, dynamometric scales, speed measurements, accelerometers, strain gauges, PIV, trajectography, etc.
References
Quality of ambient conditions
Acoustics
Our services
- Prevention of noise pollution and simulation of soundscapes close to roads and railways.
- Acoustic quality in complex indoor volumes.
- Study of the aeroacoustic behavior of structures and characterization of aeroacoustic accidents.
Methodology
- Physical study of aeroacoustic behavior, in the wind tunnel
- Digital simulation of noise exposure (ICARE-MITHRA combination)
- Realistic sound rendering by auralization, usage in cooperation with neighborhood residents
- On-site measurement of impulse responses (indoor volumes) and calculation of performance indicators (intelligibility, music listening indicators, etc.)
- Architectural diagnostics in complex spaces (open-plan offices, performance halls, etc.)
Software developed and marketed by the CSTB:
-
ICARE: acoustic simulation in complex environments.
ICARE is a simulation tool of acoustic propagation using asymptotic methods in complex 3D environments. This tool can be used for optimizing the acoustics of a performance hall and for predicting intelligibility in vehicle interiors or congested spaces. -
MITHRA: prediction of noise pollution near a structure
MITHRA is acoustic mapping software for predicting the noise exposure level at the scale of a city, using a simplified approach. It can be combined with more precise tools, such as ICARE, to predict noise pollution around a large structure.
References
Lighting
Our services
- Assessment and optimization of artificial lighting systems for visual comfort
- Assessment and optimization of the use of natural lighting
- Study of the impact on sunlight of a large structure
- Optimization of the energy consumption of lighting installations
Methodology
Internal tool developed by the CSTB:
-
PHANIE: prediction of lighting environments.
PHANIE is physical lighting simulation software, capable of processing highly complex scenes. Right from the design phase of a room or building, this software can define and visualize lighting scenarios, depending on multiple parameters: architecture, natural lighting sources and climate, lamps and light fixtures and type of materials.
Airflow and temperature
Using an experimental and / or digital approach
- Diagnosis of the discomfort caused by the wind (project and project impact)
- Characterization of local wind conditions
- The project's impact on comfort
- Proposal for aerodynamic treatments for the comfort of pedestrians and wind safety in urban environments
- Protecting the site from the wind
- Multi-criteria approach (thermal comfort, or PET: Physiological Equivalent Temperature)
- Assessment of perceived comfort
Vibration
Our services
- Study of the propagation of environmental vibrations and coupling with a structure.
Methodology
- Experimental characterization of vibration sources (rail infrastructure, worksites, etc.)
- On-site measurement of the movement of foundations
- Vibration diagnosis of structures and recommendations
- Vibration diagnosis of sites (assessment of the vibration risk in the preliminary design)
Internal tool developed by the CSTB:
-
MEFISSTO: vibration propagation in the ground and structures.
MEFISSTO is software for calculating the propagation of vibrations in the ground and in structures. It is based on complementary finite element methods (FEM/BEM) to model the foundations or structures of buildings, as well as the ground. For example, it can be used to size systems for reducing the vibrations transmitted to major structures.
Technological platforms
- Exciters are devices used to cause vibrations in footbridges, major bridges, cable-stayed bridges, etc., for dynamic characterization purposes.
References
Safety, Structures and Fire Performance
Fire safety
Our services
- Studies of fire safety engineering: defining realistic fire scenarios, actions on structures exposed to fire, stability of works in real fire conditions, smoke extraction engineering and simulation of the movement of people
- Assessment of spraying systems (water mist and sprinkler systems)
- Support for worksite assessments
- Study of the behavior of concrete at high temperatures and conducting of in situ flaking tests.
Methodology
- Carrying out full scale or in situ fire testing campaigns (in the context of fire safety rules for example).
-
SCHEMA-SI: assessing the fire safety level of a building using a stochastic approach.
SCHEMA-SI is a continuous phenomena digital simulation tool (i.e. spread of fire, movement of smoke), and discrete phenomena (i.e. human actions or activation of a system); which, using a stochastic approach, calculates an occurrence frequency of undesirable events (death of a person or property damage). It can be used both to reenact events in order to reconstruct the possible chain of events, and to design / construct, in order to optimize the choice of safety measures. -
CIFI: zone model fire simulation.
CIFI is a 2-zone model for modeling fire spreading in compartments. In particular, it can be used to calculate changes in the height of the layer of hot gases and its temperature. Thanks to its speed of operation, CIFI simulates a large number of scenarios and is therefore a useful complement to CFD models, such as FDS software. -
SEVE-P: modeling human behavior.
SEVE-P is a simulation tool for estimating the time needed for people to evacuate. It is intended for buildings open to the public, and more precisely, for large premises, such as department stores, cinemas, shopping centers, etc. This tool is combined with an application for visualizing itineraries chosen by people. SEVE-P is used, for example, for analyzing the performance of smoke extraction systems.
References
Structural diagnosis
Our services
- Assessment of the resistance capacities of structural components or complete structures
- Qualification of the degree of damage sustained by structures, after accidental events
- Inspection of the state of dilapidation of old structures
- Analysis of refurbishment and structural improvement techniques, from a technical and economic point of view
Methodology
- Combined approach: trials and digital simulation
- Calculation of advances in plasticity and elastoplasticity.
- Earthquake vulnerability
References
Our services
- Pre-diagnosis regarding the challenges involved in requalification of the structure.
- Level-one quantification of the vulnerability threshold using an advanced approach, such as pushover analysis or localized plastification, in order to calculate the structure's safety distance, after combination with the stakes.
- Analysis of reinforcement techniques, from the perspective of the variation of the ag / cost ratio. Selection of plausible techniques.
- Level-two requalification of the structure, with the reinforcements chosen and quantification of the gap that has been bridged. Choice of the reinforcement kinematics to reach the targeted threshold.
Methodology
- Combined approach: trials and digital simulation
- Calculation of advances in plasticity and elastoplasticity.
- Laboratory tests on components or materials, to establish laws of behavior.
References
Contact